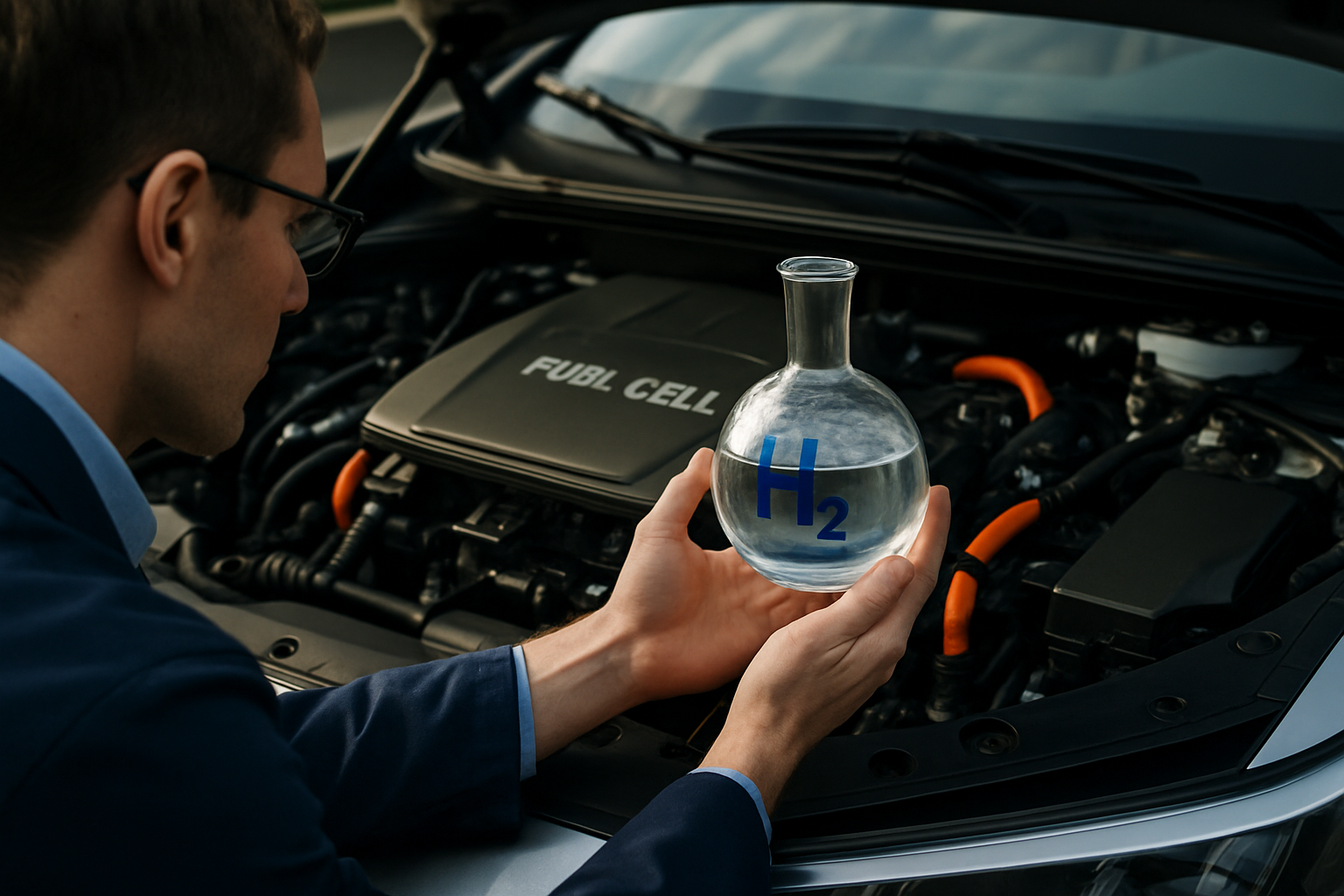
The Resurgence of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles
In the ever-evolving landscape of automotive technology, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are making a compelling comeback. Once overshadowed by battery electric alternatives, these innovative machines are now gaining traction as a promising solution for sustainable transportation. This article delves into the world of hydrogen-powered cars, exploring their cutting-edge technology, environmental benefits, and potential to reshape the future of mobility.

The Science Behind Hydrogen Fuel Cells
At the heart of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles lies a remarkable feat of engineering: the fuel cell stack. This intricate system combines hydrogen from the vehicle’s tank with oxygen from the air to produce electricity, which powers the car’s electric motor. The only byproduct of this chemical reaction is water, making hydrogen fuel cells an exceptionally clean energy source.
The fuel cell stack consists of multiple layers, each playing a crucial role in the energy conversion process. Hydrogen enters the anode side of the fuel cell, where a catalyst separates the hydrogen molecules into protons and electrons. The protons pass through a membrane to the cathode side, while the electrons are forced through an external circuit, creating an electric current. On the cathode side, oxygen combines with the protons and electrons to form water vapor, which is then expelled from the vehicle.
Infrastructure Challenges and Solutions
One of the primary hurdles facing the widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles is the lack of refueling infrastructure. Unlike battery electric vehicles, which can be charged at home or at increasingly common public charging stations, hydrogen vehicles require specialized fueling stations. However, several countries are making significant strides in addressing this challenge.
Japan, for instance, has committed to building a network of hydrogen fueling stations across the country, with plans to have 900 stations operational by 2030. Similarly, Germany aims to have 400 hydrogen stations by 2025. In the United States, California leads the charge with over 40 public hydrogen fueling stations already in operation. As more stations come online, the practicality of owning a hydrogen fuel cell vehicle increases, potentially accelerating adoption rates.
Performance and Efficiency Improvements
Recent advancements in fuel cell technology have dramatically improved the performance and efficiency of hydrogen-powered vehicles. Modern fuel cell stacks are more compact, lighter, and more durable than their predecessors, addressing many of the concerns that initially held back the technology.
One significant improvement is in the area of cold-weather performance. Early fuel cell vehicles struggled in freezing temperatures, as the water produced by the chemical reaction could freeze and damage the system. However, innovative engineering solutions, such as rapid heating systems and improved water management, have largely overcome this challenge. Today’s hydrogen fuel cell vehicles can start and operate efficiently even in sub-zero conditions.
Moreover, the overall efficiency of fuel cell systems has increased substantially. The latest generation of fuel cells can convert up to 60% of the energy in hydrogen into electricity, compared to around 25% for a typical gasoline engine. This high efficiency, combined with the energy density of hydrogen, allows for impressive driving ranges of 300 miles or more on a single tank.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
While hydrogen fuel cell vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, the environmental impact of hydrogen production is a critical factor to consider. Currently, most hydrogen is produced through steam methane reforming, a process that uses natural gas and releases carbon dioxide. However, the push towards green hydrogen production methods is gaining momentum.
Electrolysis, which uses electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen, is becoming increasingly viable as renewable energy sources become more prevalent and cost-effective. When powered by solar or wind energy, this process can produce truly zero-emission hydrogen. Several countries and companies are investing heavily in green hydrogen production facilities, paving the way for a sustainable hydrogen economy.
The Role of Hydrogen in Commercial Transportation
While much attention has been focused on passenger vehicles, hydrogen fuel cell technology is making significant inroads in the commercial transportation sector. Long-haul trucking, in particular, stands to benefit greatly from hydrogen power. The quick refueling times and long range of hydrogen fuel cell trucks make them an attractive alternative to battery electric options for heavy-duty applications.
Companies like Hyundai and Toyota are already testing hydrogen-powered semi-trucks on public roads, with promising results. These vehicles can carry heavier loads over longer distances than their battery electric counterparts, all while producing zero emissions. As the technology matures and infrastructure expands, we may see a significant shift towards hydrogen power in the logistics industry.
The Future of Hydrogen Mobility
As we look to the future, the potential of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles extends far beyond cars and trucks. Research is underway to develop hydrogen-powered trains, ships, and even aircraft. The versatility of hydrogen as an energy carrier makes it a compelling option for decarbonizing various modes of transportation.
The coming years will likely see continued innovation in fuel cell technology, further improving efficiency, durability, and cost-effectiveness. As production scales up and economies of scale come into play, the price of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles is expected to decrease, making them more accessible to a broader range of consumers.
In conclusion, the resurgence of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles represents a significant shift in the automotive landscape. With their combination of zero emissions, quick refueling times, and long-range capabilities, these vehicles offer a compelling vision for the future of sustainable transportation. As technology advances and infrastructure expands, hydrogen power may well play a crucial role in reshaping our mobility ecosystem, driving us towards a cleaner, more sustainable future.