Telecom-as-a-Service: Revolutionizing Business Connectivity
The telecommunications industry is undergoing a seismic shift as businesses seek more flexible, scalable, and cost-effective connectivity solutions. Enter Telecom-as-a-Service (TaaS), a groundbreaking model that's redefining how organizations approach their communication needs. But what exactly is TaaS, and how is it transforming the landscape of business connectivity? Let's dive into this innovative approach that's catching the attention of IT leaders and telecom experts worldwide.
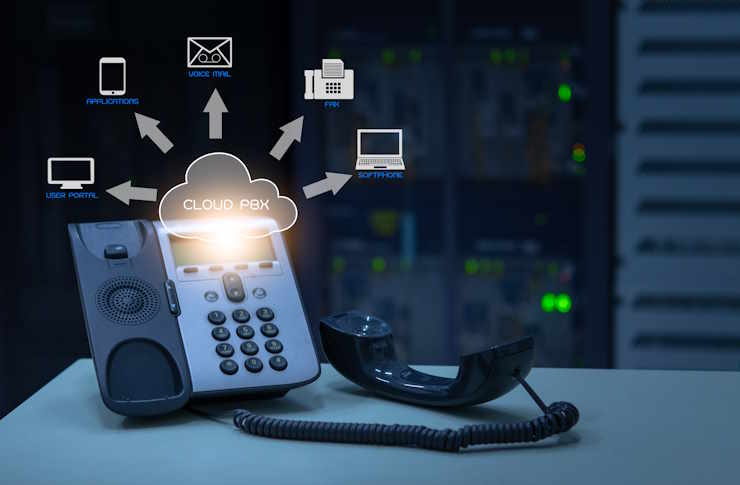

In a TaaS model, service providers offer a comprehensive suite of telecom services, including voice, data, video, and unified communications, all delivered over the cloud. Businesses can then subscribe to these services based on their specific needs, scaling up or down as required. This flexibility is particularly appealing in today’s fast-paced business environment, where agility and adaptability are key to staying competitive.
The Evolution of Telecom Services
To fully appreciate the impact of TaaS, it’s essential to understand the evolution of telecom services. Traditionally, businesses had to invest heavily in on-premises telecom infrastructure, including PBX systems, dedicated lines, and hardware. This approach required significant capital expenditure and often resulted in overprovisioning to accommodate future growth.
As technology advanced, managed services emerged, offering businesses more flexibility and reducing the burden of managing complex telecom systems. However, these solutions still often involved long-term contracts and limited scalability. The rise of cloud computing and software-defined networking paved the way for more agile solutions, ultimately leading to the development of TaaS.
Key Benefits of Telecom-as-a-Service
The TaaS model offers numerous advantages over traditional telecom approaches:
-
Cost Efficiency: By eliminating the need for large upfront investments in hardware and infrastructure, TaaS allows businesses to shift from a capital expenditure (CapEx) model to an operational expenditure (OpEx) model. This not only frees up capital but also makes costs more predictable and easier to manage.
-
Scalability and Flexibility: TaaS enables businesses to scale their telecom services up or down based on their current needs. This flexibility is particularly valuable for companies with seasonal fluctuations or rapid growth trajectories.
-
Access to Advanced Technologies: TaaS providers typically offer the latest telecom technologies and features as part of their service offerings. This allows businesses to stay current with technological advancements without the need for constant upgrades to their own infrastructure.
-
Simplified Management: With TaaS, the service provider takes on the responsibility of maintaining and upgrading the telecom infrastructure. This reduces the burden on in-house IT teams and allows them to focus on more strategic initiatives.
-
Enhanced Reliability and Security: Leading TaaS providers invest heavily in robust infrastructure and security measures, often surpassing what individual businesses could achieve on their own.
Implementing TaaS: Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of TaaS are compelling, implementing this model comes with its own set of challenges and considerations:
-
Network Dependency: TaaS relies heavily on a stable and high-performance internet connection. Businesses must ensure their network infrastructure can support the increased demands of cloud-based telecom services.
-
Security and Compliance: As with any cloud-based service, security is a top concern. Organizations must carefully evaluate the security measures and compliance certifications of potential TaaS providers, especially in industries with strict regulatory requirements.
-
Integration with Existing Systems: Migrating to a TaaS model may require integration with existing business systems and processes. This can be complex and may require careful planning and execution.
-
Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Given the critical nature of telecom services, businesses must carefully review and negotiate SLAs with TaaS providers to ensure adequate performance, reliability, and support.
-
Vendor Lock-in: While TaaS offers flexibility, businesses should be mindful of potential vendor lock-in. It’s important to consider the ease of migrating to another provider if needed.
The Future of TaaS and Business Connectivity
As businesses continue to embrace digital transformation, the demand for flexible, scalable, and cost-effective telecom solutions is only expected to grow. TaaS is well-positioned to meet these needs and is likely to see widespread adoption in the coming years.
Several trends are shaping the future of TaaS:
-
AI and Machine Learning Integration: TaaS providers are increasingly incorporating AI and machine learning capabilities to optimize network performance, predict and prevent issues, and deliver more personalized services.
-
Enhanced Collaboration Tools: With the rise of remote and hybrid work models, TaaS offerings are expanding to include more sophisticated collaboration tools and unified communications platforms.
-
Network Slicing: As 5G networks become more prevalent, TaaS providers may leverage network slicing technology to offer customized, high-performance connectivity solutions for specific business needs.
-
Edge Computing Integration: TaaS may evolve to incorporate edge computing capabilities, enabling lower latency and improved performance for certain applications.
-
Sustainability Focus: As businesses prioritize sustainability, TaaS providers may differentiate themselves by offering eco-friendly solutions and helping customers reduce their carbon footprint through optimized telecom infrastructure.
The telecommunications landscape is rapidly evolving, and Telecom-as-a-Service represents a significant shift in how businesses approach their connectivity needs. By offering flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency, TaaS is empowering organizations to stay agile and competitive in an increasingly digital world. As the technology continues to mature and evolve, it’s clear that TaaS will play a crucial role in shaping the future of business connectivity.