Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis: Revolutionizing Body Composition Assessment
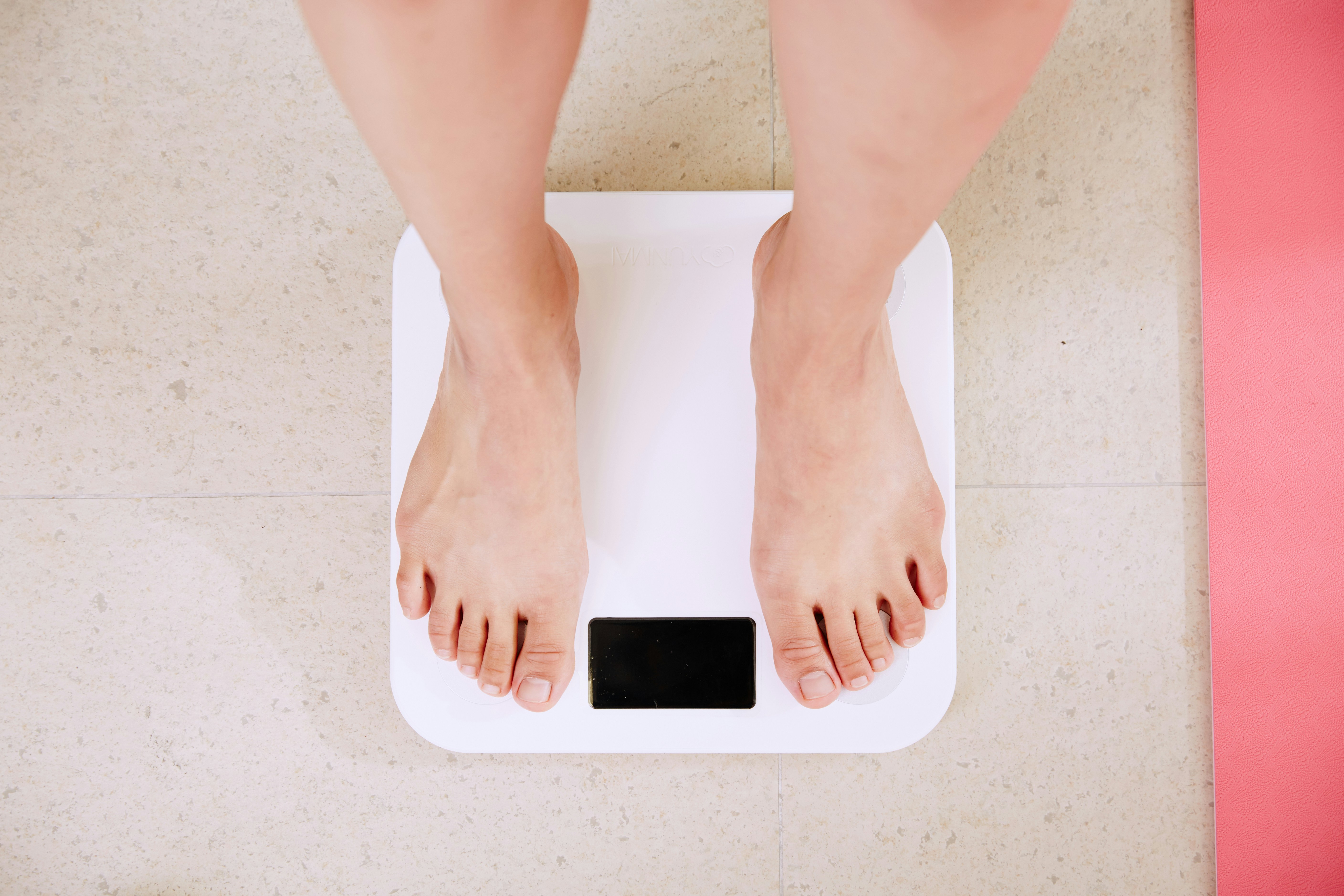
Is your bathroom scale telling you the whole story about your health? What if there was a way to peek beneath the surface and understand your body's true composition? Enter the world of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA), a cutting-edge technology that's transforming how we measure and interpret our body's makeup.
Lean tissue, which is primarily composed of water and electrolytes, is a good conductor of electricity. Fat tissue, on the other hand, contains less water and acts as an insulator, providing more resistance to the electrical current. By analyzing these differences in electrical conductivity, BIA devices can estimate the proportions of fat mass, lean mass, and total body water with remarkable accuracy.
Historical Context and Evolution
The concept of using electrical properties to measure body composition dates back to the 1960s, but it wasn’t until the 1980s that BIA began to gain traction in clinical and research settings. Early BIA devices were large, expensive, and primarily used in hospitals and research laboratories. However, as technology advanced, BIA became more accessible and user-friendly.
In the 1990s, the first consumer-grade BIA scales hit the market, bringing this sophisticated technology into homes. Today, BIA is used in a wide range of applications, from fitness centers and nutrition clinics to professional sports teams and space agencies monitoring astronauts’ health.
Benefits and Applications of BIA
BIA offers several advantages over traditional methods of body composition assessment:
-
Non-invasive and painless: Unlike methods like hydrostatic weighing or DEXA scans, BIA is quick and comfortable for the user.
-
Comprehensive data: BIA provides detailed information about fat mass, lean mass, muscle mass, bone mass, and hydration levels.
-
Tracking progress: Regular BIA measurements allow individuals to monitor changes in their body composition over time, which is particularly useful for fitness and weight management goals.
-
Identifying health risks: By revealing the ratio of fat to lean mass, BIA can help identify potential health risks associated with excess body fat or muscle loss.
-
Customizing nutrition and exercise plans: The detailed body composition data from BIA can be used to tailor diet and exercise regimens to individual needs.
Challenges and Limitations
While BIA offers numerous benefits, it’s important to understand its limitations:
-
Hydration affects results: BIA measurements can be influenced by hydration status, so it’s crucial to maintain consistent hydration levels for accurate comparisons over time.
-
Variability between devices: Different BIA devices may use varying algorithms, leading to discrepancies in results between machines.
-
Not suitable for everyone: BIA may not be appropriate for individuals with certain medical conditions or implanted electronic devices like pacemakers.
-
Interpretation complexity: Understanding and interpreting BIA results often requires professional guidance to ensure accurate conclusions are drawn.
The Future of BIA in Health and Wellness
As technology continues to advance, the future of BIA looks promising. Emerging trends include:
-
Integration with wearable devices: BIA technology is being incorporated into smartwatches and fitness trackers, allowing for continuous body composition monitoring.
-
Artificial Intelligence integration: AI algorithms are being developed to analyze BIA data more comprehensively, providing personalized health insights and recommendations.
-
Expanded health applications: Researchers are exploring the use of BIA in detecting and monitoring various health conditions, including lymphedema and certain types of cancer.
-
Enhanced accuracy: Ongoing research is focusing on improving the accuracy of BIA measurements across diverse populations and body types.
Practical Applications in Daily Life
Optimizing Your BIA Experience
-
Measure at consistent times, preferably in the morning before eating or drinking
-
Stay hydrated, but avoid excessive fluid intake before measurement
-
Avoid alcohol and intense exercise for 24 hours prior to testing
-
Use the same device for all measurements to ensure consistency
-
Consider seasonal variations in body composition when interpreting results
-
Combine BIA data with other health metrics for a comprehensive health assessment
In conclusion, Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis represents a significant leap forward in our ability to understand and monitor body composition. By providing detailed insights into our body’s makeup, BIA empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health and fitness goals. As this technology continues to evolve and integrate with other health monitoring tools, it promises to play an increasingly important role in personalized health management and preventive care strategies. Embracing BIA as part of a holistic approach to health can open new doors to achieving optimal wellness and longevity.